Temperature management has a very basic role in modern industrial operations for the achievement of seamless operations and high-quality products. The major equipment used for this purpose is known as industrial process water chillers. Applications include food & beverage processing, chemical production, electronic component manufacturing, and medical apparatus cooling. However, most people don’t understand its operation and importance. Herein, we shall discuss the working principle, types, and wide applications of industrial process chillers within the industry to ensure you get acquainted with this very significant machine.
Ⅰ. Working Principle
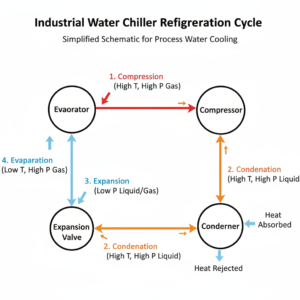
An industrial water cooling unit is a particular machine whose purpose is to cool down the heat that has been generated in industrial production processes. In simple terms, it lowers the temperature of process water to the preferred levels via a refrigeration system. This guarantees stability in the production process as well as ensuring product quality. It runs on a refrigeration cycle, mainly involving the following steps:
Refrigerant Compression: The refrigerant is compressed by the compressor, increasing its temperature and pressure to transform it into a high-temperature, high-pressure gas.
Condensation Process: The high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant gas enters the condenser, where it exchanges heat with a cooling medium (such as air or water), releases heat, and liquefies.
Expansion Process: The liquid refrigerant passes through an expansion valve into the evaporator. Here, pressure decreases, causing the refrigerant to rapidly vaporize and absorb a significant amount of heat.
Evaporation Process: The refrigerant absorbs heat from the process water within the evaporator, lowering its temperature to achieve cooling.
This refrigeration cycle repeats continuously, ensuring the process water temperature remains within the set range. The highly efficient cooling capability of industrial process water chillers makes them essential in industrial sectors requiring precise temperature control.
Ⅱ. Types of Industrial Process Water Chillers
Based on varying cooling demands and application scenarios, industrial process water units can be categorized into multiple types. Each type features distinct design and performance characteristics to meet diverse industrial production needs.
1. 空冷式チラー
Air-cooled industrial water cooling units draw ambient air into the condenser via fans, utilizing airflow to dissipate heat from the refrigerant. This type features a simple structure and easy installation, eliminating the need for complex cooling water systems. Consequently, they are highly popular in small to medium-sized industrial applications. However, air-cooled chillers exhibit relatively lower heat dissipation efficiency, and their performance may be impacted in high-temperature or high-humidity environments.
2. Water-Cooled Chillers
Water-cooled industrial chillers sent water when the condenser needed a way to throw off extra heat from the outside. This type has a simple build and is easy to put in place since it does not need any complex parts for systems of cooling water. Because of this, they are very common in small to medium-sized uses in industry. But air-cooled chillers have less than optimal efficiency when getting rid of heat; their work can be affected if used in hot or wet conditions.
3. Evaporative Condensed Chillers
Evaporative Condensing Chillers Evaporative condensing chillers support industrial process water by running both air and water systems. They use the evaporation of water to achieve better efficiency in cooling, thus supporting more efficient heat dissipation. This type of chiller attains very high performance in certain specific applications within industry, particularly where the climate has moderate temperature and humidity.
Ⅲ. Advantages and Challenges of Industrial Process Water Chillers
1. Advantages
Industrial process water chillers offer significant advantages in modern industrial production
- Highly effective cooling: It lowers the temperature of process water in a high-load industry.
- Precise Control: Allows accurate setting of the process water temperature through an advanced control system.
- Adaptability: Multiple choices provide solutions for different scales and environments where cooling is required.
- High Reliability: A mature design ensures stable operation for a long period of running hours.
- Energy-saving potential: Some newer chillers incorporate energy-efficient technologies to reduce consumption.
2. Challenges of the industrial water cooling unit
Despite their capabilities, industrial process water chillers face certain challenges:
- High initial investment costs: Particularly for water-cooled and evaporative condenser chillers, which require substantial equipment and installation expenses.
- Complex maintenance requirements: Regular upkeep of refrigeration and cooling water systems is essential for long-term stable operation.
- Energy consumption concerns: Some chillers exhibit high operational energy usage, necessitating energy-saving measures.
Ⅳ. 結論
Industrial water cooling units have become essential equipment in the contemporary industrial production landscape. The system operates efficiently and supports multi-application processes, which implies that it applies to varying fields of industry. It has applications among producers in the food and beverage industry, electronics manufacturing companies, chemical processing plants, and medical device product manufacturers to help maintain steady operations and high product quality. Industrial technology development leads to the continuous evolution of these chillers towards meeting increased production requirements. Thus, in a prospective industrial process, water chillers shall be imperative instruments ensuring smooth, efficient operation of more industries.